Garbino is a warm, dry wind that descends down mountains, affecting specific regions worldwide. Unlike typical foehn winds, Garbino possesses unique characteristics and impacts, making it a fascinating meteorological phenomenon. This article delves into the intricacies of Garbino, exploring its formation, characteristics, and notable occurrences.
What is a Garbino Wind?
Garbino, often referred to as a “descending wind,” originates from high-pressure systems in mountainous areas. As air masses descend the slopes, they undergo adiabatic compression, leading to a rise in temperature and decrease in humidity. This process differentiates Garbino from other winds, giving it its characteristic warmth and dryness.
Formation and Characteristics of Garbino
The formation of Garbino hinges on the interaction between topography and atmospheric pressure. When high-pressure systems settle over mountainous regions, air masses are forced to descend the slopes. As the air descends, it gets compressed due to increasing atmospheric pressure. This compression results in adiabatic heating, causing the air temperature to rise at a rate of approximately 10°C per 1000 meters of descent.
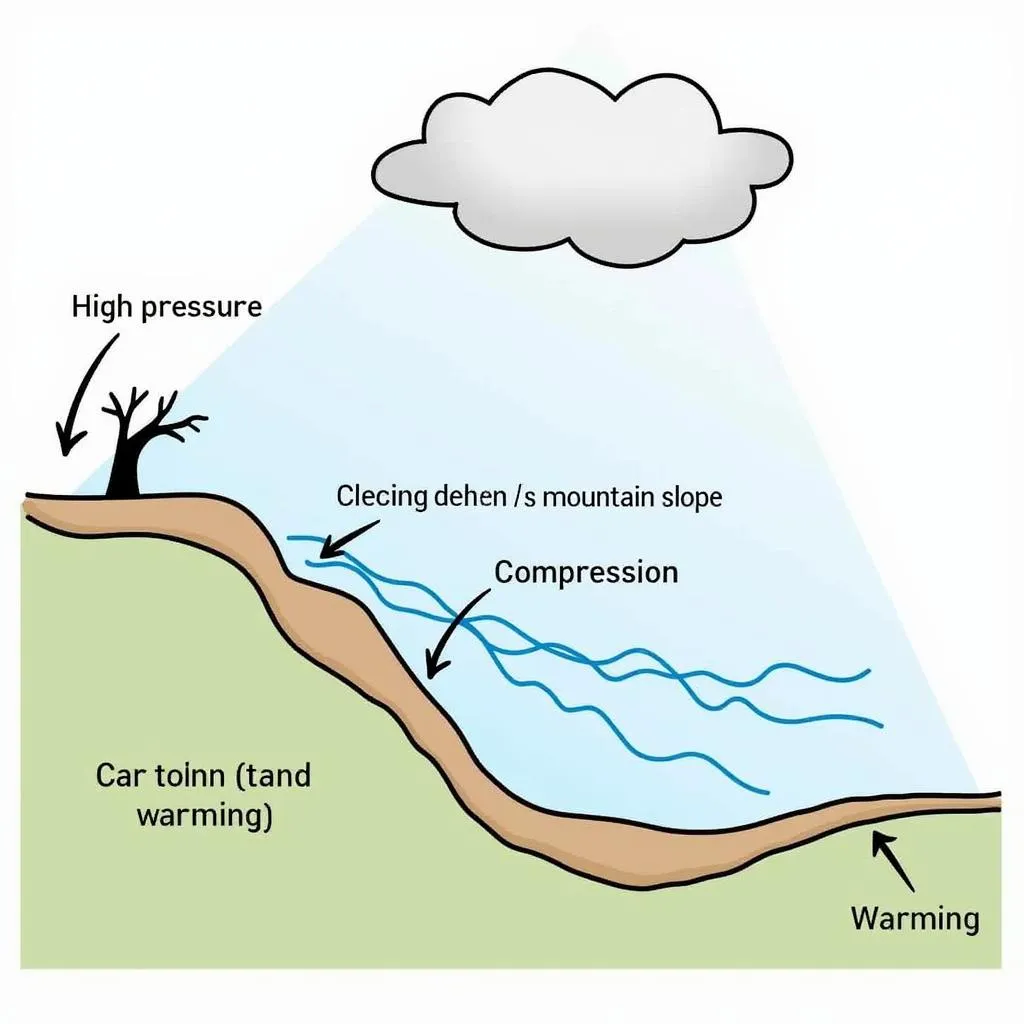 Garbino Formation Process
Garbino Formation Process
Simultaneously, the descending air mass loses its capacity to hold moisture as it warms. This leads to a decrease in relative humidity, making Garbino exceptionally dry. The combination of high temperatures and low humidity creates a unique microclimate in the affected regions.
Distinguishing Garbino from Other Winds
While Garbino shares similarities with foehn winds, several key differences set them apart. Firstly, Garbino winds are often stronger and gustier than their foehn counterparts. Secondly, the temperature increase associated with Garbino is typically more significant due to the steeper slopes involved. Lastly, Garbino winds often occur during specific seasons or weather patterns, making them more predictable in certain regions.
 Garbino vs. Foehn Winds
Garbino vs. Foehn Winds
Notable Occurrences and Impacts of Garbino
Garbino winds are experienced in various parts of the world, each with its distinct characteristics and impacts.
- North America: The Santa Ana winds in Southern California are a prime example of Garbino. These winds, notorious for their strength and dryness, contribute significantly to wildfire risk in the region.
- Europe: The Garbino winds in the Adriatic Sea region, particularly along the Croatian coast, are known for their sudden temperature fluctuations and impact on local weather patterns.
- South America: Similar winds, known as Zonda winds, affect the eastern slopes of the Andes Mountains, bringing hot, dry conditions to western Argentina.
Impact on Human Activities
Garbino winds can significantly impact human activities, particularly agriculture, transportation, and human health. The warm, dry air can lead to rapid evaporation, stressing crops and increasing irrigation needs. Strong winds can disrupt air and sea travel, posing challenges for transportation. Additionally, the sudden temperature changes and dry air associated with Garbino can exacerbate respiratory problems and trigger allergies in sensitive individuals.
 Garbino Impact on Agriculture
Garbino Impact on Agriculture
Conclusion
Garbino, a unique meteorological phenomenon, exemplifies the intricate relationship between topography and atmospheric processes. Its characteristic warmth, dryness, and localized occurrence make it a significant factor influencing weather patterns and human activities in specific regions globally. Understanding Garbino’s intricacies is crucial for mitigating its potential impacts and adapting to the challenges it poses.
FAQs
-
What is the main difference between Garbino and Foehn winds?
Garbino winds are generally stronger and drier than Foehn winds, with a more pronounced temperature increase. -
Where are Garbino winds most commonly experienced?
Garbino winds occur in various regions, including North America (Santa Ana winds), Europe (Adriatic coast), and South America (Zonda winds). -
How can Garbino winds impact agriculture?
The warm, dry air associated with Garbino can lead to rapid evaporation, stressing crops and increasing the need for irrigation. -
Do Garbino winds pose any risks to human health?
Yes, the sudden temperature changes and dry air associated with Garbino can exacerbate respiratory problems and allergies. -
Are Garbino winds predictable?
Garbino winds often occur during specific seasons or weather patterns, making them more predictable in certain regions.
Need Assistance?
For any inquiries or assistance, contact us at:
Phone Number: 0902476650
Email: [email protected]
Address: 139 Đ. Võ Văn Kiệt, Hoà Long, Bà Rịa, Bà Rịa – Vũng Tàu, Việt Nam.
Our customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you.





