Above Board Electronics play a crucial role in numerous applications, from consumer devices to industrial machinery. Understanding their significance, types, and applications can be invaluable for hobbyists, engineers, and anyone interested in the world of electronics.
What are Above Board Electronics?
Above board electronics, also known as through-hole electronics, refer to electronic components designed for insertion through pre-drilled holes on a printed circuit board (PCB). Unlike their surface-mount technology (SMT) counterparts, which are placed directly on the PCB surface, above board components have leads that extend through the board, allowing for soldering on the opposite side. This traditional method of assembly offers several distinct advantages and remains relevant in various electronic designs.
Advantages of Above Board Electronics
-
Durability and Strength: The through-hole mounting technique provides a more robust physical connection compared to SMT. This makes above board electronics well-suited for applications that experience significant vibration, mechanical stress, or extreme temperatures.
-
Ease of Prototyping and Repair: The larger size and accessible leads of above board components simplify manual prototyping and debugging. Additionally, replacing faulty components is generally easier with through-hole technology.
-
Higher Current Handling: The leads of above board components offer a larger surface area for soldering, enabling them to handle higher currents compared to similarly sized SMT components.
Common Types of Above Board Electronics
The world of above board electronics encompasses a diverse range of components, each fulfilling specific functions within a circuit. Let’s delve into some of the most prevalent types:
-
Resistors: These passive components are essential for controlling current flow within a circuit. They are available in various resistance values and power ratings to suit different applications.
-
Capacitors: These components store and release electrical energy, playing a crucial role in filtering, smoothing, and timing circuits. Like resistors, capacitors come in diverse capacitance values and voltage ratings.
-
Diodes: As unidirectional devices, diodes allow current to flow in only one direction, making them vital for rectification, signal clipping, and voltage regulation.
-
Transistors: These semiconductor devices amplify or switch electronic signals, forming the building blocks of amplifiers, oscillators, and digital logic circuits.
-
Integrated Circuits (ICs): These complex circuits, often referred to as “chips,” integrate numerous transistors, resistors, and other components onto a single semiconductor die. ICs perform a wide array of functions, from simple logic operations to complex data processing.
Applications of Above Board Electronics
The inherent advantages of above board electronics make them suitable for a broad spectrum of applications:
-
High-Power Applications: The superior current handling capability of above board components makes them ideal for applications involving high currents, such as power supplies, motor controllers, and audio amplifiers.
-
Industrial Equipment: The robustness of above board electronics makes them well-suited for the demanding environments often encountered in industrial settings, where they are used in automation systems, control panels, and sensor interfaces.
-
Automotive Electronics: The ability to withstand vibration and temperature fluctuations makes above board components suitable for automotive applications, including engine control units, lighting systems, and dashboard electronics.
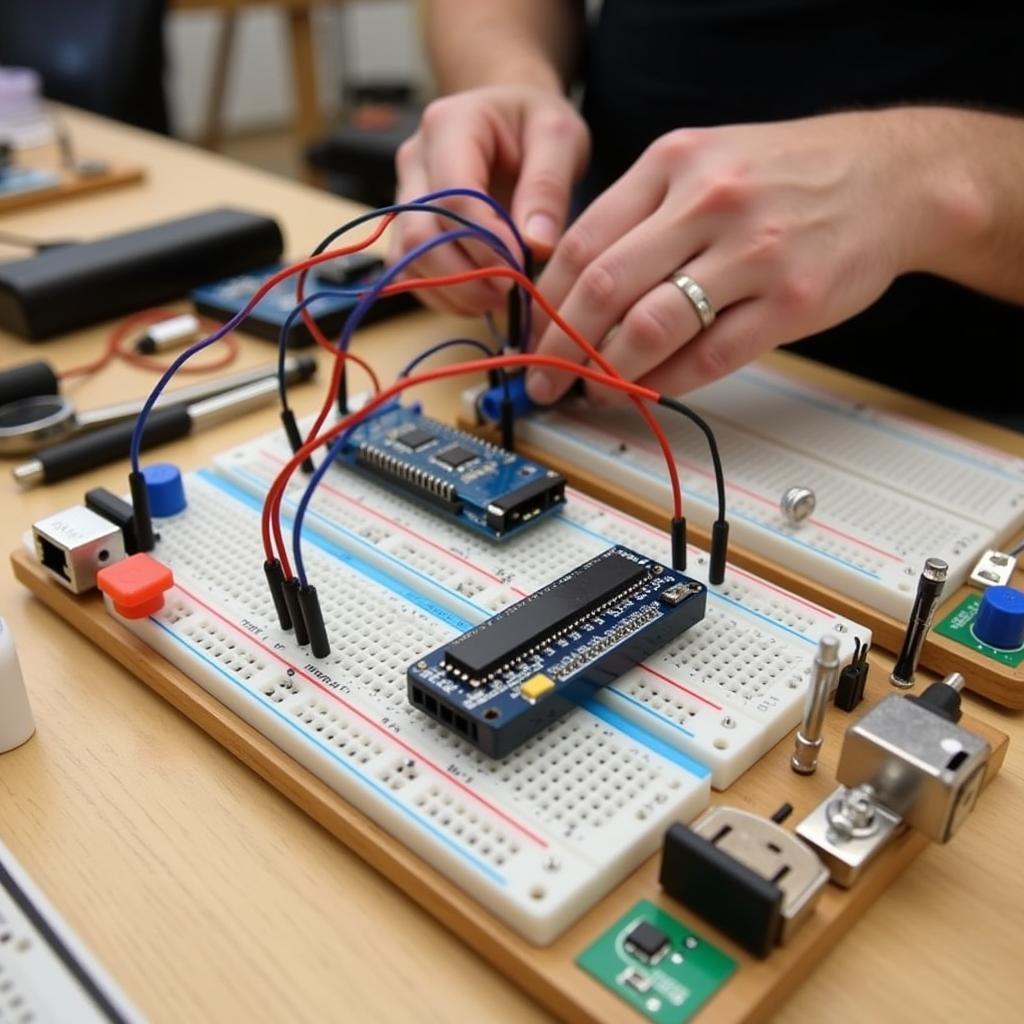 Above Board Electronics in Prototyping
Above Board Electronics in Prototyping
- Prototyping and Hobbyist Projects: The ease of assembly and debugging makes above board electronics a popular choice for prototyping, hobbyist projects, and educational purposes.
Conclusion
Above board electronics continue to hold a significant place in the electronics industry, offering a reliable and robust solution for various applications. Their durability, ease of use, and suitability for high-power applications ensure their relevance in a world increasingly dominated by miniaturization. Understanding the characteristics and applications of above board electronics empowers designers, engineers, and enthusiasts to make informed decisions when selecting components for their projects.
FAQs
What are the main advantages of using above board electronics?
Above board electronics offer greater durability, easier prototyping and repair, and higher current handling capabilities compared to surface-mount alternatives.
What are some common applications for above board electronics?
They are frequently used in high-power applications, industrial equipment, automotive electronics, prototyping, and hobbyist projects.
Are above board electronics still relevant today?
Yes, despite the rise of surface-mount technology, above board electronics remain relevant due to their advantages in specific applications.
What factors should I consider when choosing between above board and surface-mount components?
Key factors include the required current handling, mechanical stress tolerance, assembly process complexity, and overall cost considerations.
Where can I learn more about specific above board electronic components?
Numerous online resources, datasheets, and tutorials provide detailed information about individual components and their characteristics.
Need assistance with your electronics project? Contact us at Phone Number: 0902476650, Email: [email protected] Or visit our address: 139 Đ. Võ Văn Kiệt, Hoà Long, Bà Rịa, Bà Rịa – Vũng Tàu, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.





