The Hockey 1-3-1 Trap is a defensive system designed to slow down the opposing team’s offensive rush and disrupt their passing lanes. It relies on positioning and disciplined execution to effectively stifle offensive pressure. This comprehensive guide will dive deep into the intricacies of the 1-3-1, explaining its core principles, player roles, advantages, disadvantages, and how to implement it successfully.
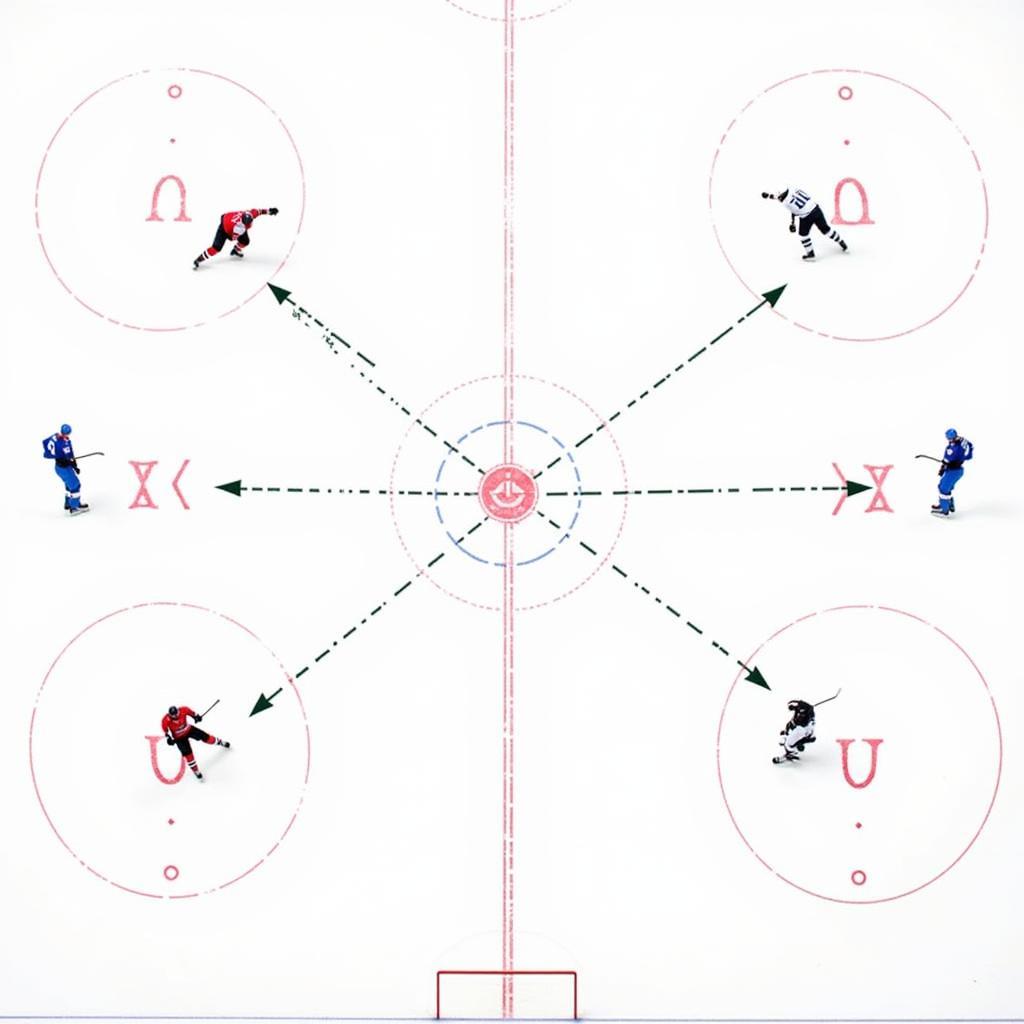 Diagram illustrating the positioning of players in a 1-3-1 trap formation
Diagram illustrating the positioning of players in a 1-3-1 trap formation
Understanding the 1-3-1 Trap: Core Principles and Player Roles
The 1-3-1 trap derives its name from the positional layout of the defensive players. One forward (F1) positions themselves high in the offensive zone, typically near the center red line. This forward acts as the first line of defense, pressuring the puck carrier and attempting to force them to dump the puck or make a risky pass. trap emp Three players (two forwards (F2, F3) and one defenseman (D1)) form a line across the neutral zone, creating a “trap” to intercept passes and disrupt the opposing team’s flow. The final defenseman (D2) stays deep in the defensive zone, protecting against breakaways and providing support to the other defenders.
Player Responsibilities
- F1 (Forward 1): The point man, responsible for applying pressure and directing the play to the sides.
- F2 & F3 (Forwards 2 & 3): Wingers in the neutral zone, focused on intercepting passes and preventing the puck from entering the defensive zone.
- D1 (Defenseman 1): The rover, supporting the forwards in the neutral zone and covering the center lane.
- D2 (Defenseman 2): The last line of defense, protecting the net and covering for the other defenders.
 Players executing the 1-3-1 trap against an attacking team
Players executing the 1-3-1 trap against an attacking team
Advantages and Disadvantages of the 1-3-1
The 1-3-1 offers several benefits when executed correctly, including:
- Frustrating the Opposition: The trap can disrupt offensive rhythm and create turnovers.
- Limiting Scoring Chances: By controlling the neutral zone, the 1-3-1 restricts the opponent’s ability to generate high-quality scoring opportunities.
- Creating Odd-Man Rushes: Turnovers generated by the trap can lead to quick counter-attacks and odd-man rushes.
However, the 1-3-1 also has its drawbacks:
- Vulnerability to Stretch Passes: Long passes can bypass the trap, leaving the defense exposed.
- Requires Discipline and Communication: Effective execution requires precise positioning and constant communication between players.
- Can Be Physically Demanding: Players cover a lot of ice, especially the forwards in the neutral zone.
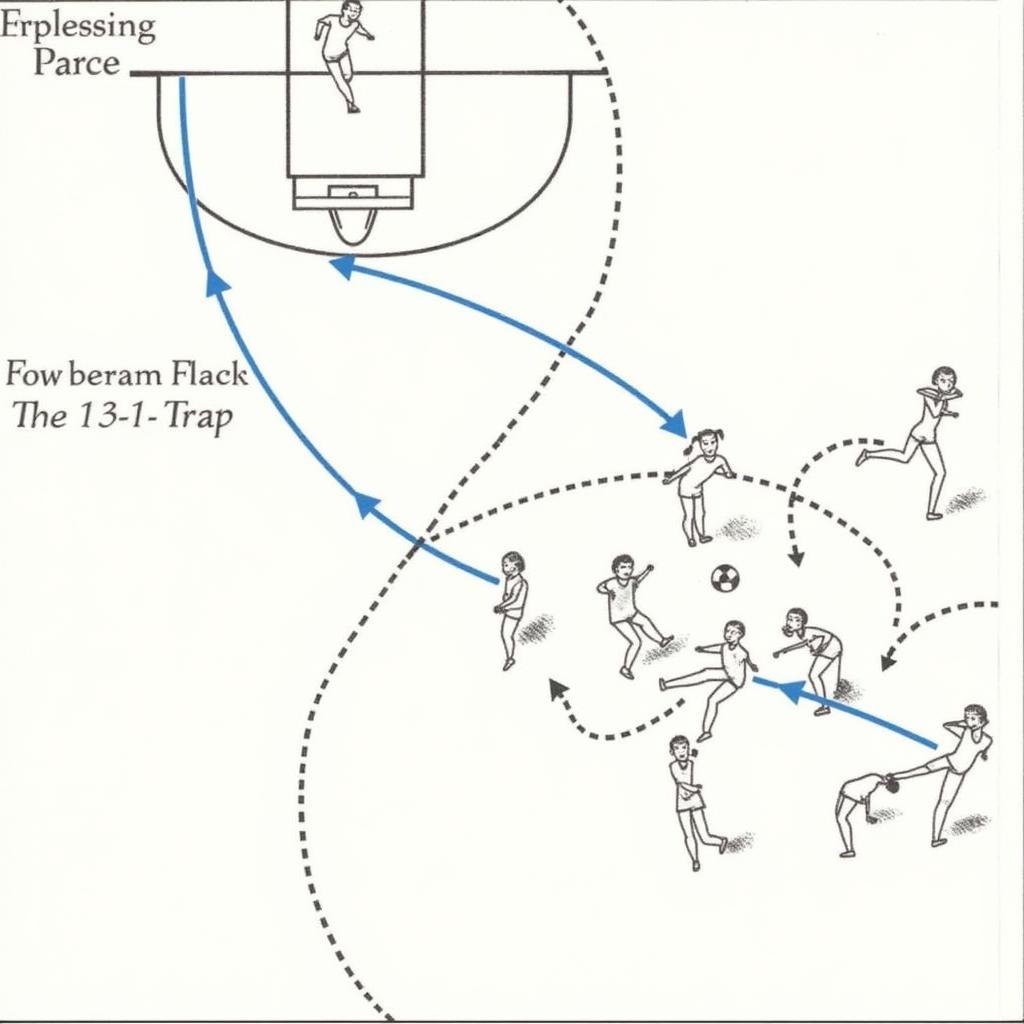 A counter-attack opportunity created by a successful 1-3-1 trap
A counter-attack opportunity created by a successful 1-3-1 trap
Implementing the 1-3-1 Effectively: Key Considerations
Successful implementation of the 1-3-1 trap hinges on several key factors:
- Coordinated Positioning: Maintaining proper spacing between players is crucial for trapping effectiveness. trap emp
- Relentless Pressure: The F1 must consistently pressure the puck carrier to force mistakes.
- Active Sticks and Interceptions: Defenders in the neutral zone need to be active with their sticks, anticipating passes and making interceptions.
- Communication: Constant communication between players is essential for adjusting to the opponent’s movements and maintaining the trap’s integrity.
“The 1-3-1 is all about communication and anticipation,” says renowned hockey coach, Alex Tremblay. “If players aren’t on the same page, the system can break down quickly.”
Conclusion: Mastering the 1-3-1 Trap
The hockey 1-3-1 trap is a complex but effective defensive strategy that can significantly impact a game’s outcome. By understanding its principles, player roles, and key considerations for implementation, coaches and players can effectively utilize the 1-3-1 to disrupt opponents and create scoring opportunities. Mastering this defensive system requires practice, discipline, and communication, but the rewards can be substantial.
FAQ
- What is the main purpose of the 1-3-1 trap? To slow down the opposing team’s attack and create turnovers.
- What are the key player roles in the 1-3-1? F1 (point man), F2 & F3 (wingers), D1 (rover), D2 (last line of defense).
- What is the biggest weakness of the 1-3-1? Vulnerability to stretch passes that bypass the trap.
- What is crucial for the 1-3-1 to be effective? Consistent pressure, active sticks, communication, and disciplined positioning.
- Is the 1-3-1 suitable for all teams? While effective, it requires specific player skills and team coordination.
- How can I improve my team’s execution of the 1-3-1? Practice, film analysis, and constant communication during games.
- What are some alternative defensive strategies? Man-to-man, zone defense, and the 2-1-2 forecheck.
Scenarios:
- Opponent breaks through the initial F1 pressure: F2 and F3 must immediately close in to prevent a clear entry into the defensive zone.
- Long pass bypasses the trap: D2 must be ready to defend against the breakaway or odd-man rush.
Further Reading:
For more information on defensive strategies, check out our article on trap emp.
Need help? Contact us 24/7: Phone: 0902476650, Email: [email protected], or visit us at 139 Đ. Võ Văn Kiệt, Hoà Long, Bà Rịa, Bà Rịa – Vũng Tàu, Việt Nam.





